Melanoma / Skin Cancer
Your Body is Your Temple
Research, Resources & Education
Table of Contents
Melanoma is a deadly cancer that can spread quickly. Catching it early increases your chances of fighting back successfully. Those at higher risk include people with fair skin, a family history of skin cancer, and weakened immune systems. Preventative measures can be taken by wearing protective clothing and avoiding sun exposure.
Information and pictures from National Cancer Institute unless otherwise specified
Skin Anatomy & Types of Cells
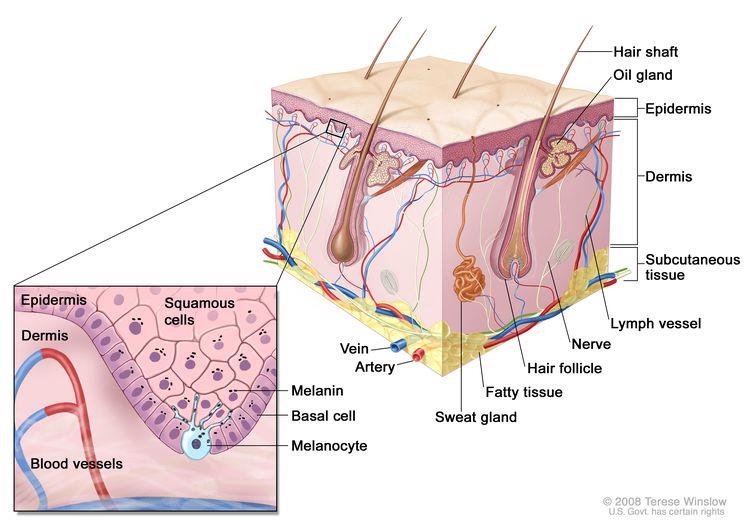
The skin is the body’s largest organ.
- It protects against heat, sunlight, injury, and infection.
- Skin also helps control body temperature and stores water, fat, and vitamin D.
- The skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis (upper or outer layer) and the dermis (lower or inner layer).
Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells:
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis.
- Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its natural color.
- When skin is exposed to the sun or artificial light, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
Melanoma & Non-Melanoma Videos
YouTube Videos that help explain types of Skin Cancer & Melenoma.
Disclaimer:
This is for research only and Lost Temple Fitness & Cancer does not endorse any video presented on this website.
It is advised that you ALWAYS CHECK WITH YOUR PHYSICIAN for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Skin Cancer / Melenoma
Melanoma vs. Non-Melanoma (Basil Cell Carcinoma)
There are different types of cancer that start in the skin. There are two forms of skin cancer: melanoma and nonmelanoma.
- Melanoma is a rare form of skin cancer.
- It is more likely to invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body than other types of skin cancer.
- When melanoma starts in the skin, it is called cutaneous melanoma.
- Melanoma may also occur in mucous membranes (thin, moist layers of tissue that cover surfaces such as the lips).
- Nonmelanoma: The most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
- They are nonmelanoma skin cancers.
- Nonmelanoma skin cancers rarely spread to other parts of the body.
Melanoma can occur anywhere on the skin.
- In men, melanoma is often found on the trunk (the area from the shoulders to the hips) or the head and neck.
- In women, melanoma forms most often on the arms and legs.
- When melanoma occurs in the eye, it is called intraocular or ocular melanoma.
Treatments
Also see Treatments
Vaccine therapy uses a substance or group of substances meant to cause the immune system to respond to a tumor and kill it.
- Vaccine therapy is being studied in the treatment of stage III melanoma that can be removed by surgery.
Surgery to remove the tumor is the primary treatment of all stages of melanoma.
- A wide local excision is used to remove the melanoma and some of the normal tissue around it.
- Skin grafting (taking skin from another part of the body to replace the skin that is removed) may be done to cover the wound caused by surgery.
- After the doctor removes all the melanoma that can be seen at the time of the surgery, some patients may be given chemotherapy after surgery to kill any cancer cells that are left.
- Surgery to remove cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes, lung, gastrointestinal (GI) tract, bone, or brain may be done to improve the patient’s quality of life by controlling symptoms.
It is important to know whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- Lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy are done to check for cancer in the sentinel lymph node during surgery (see sentinel and axillary lymph node dissection).
- A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells.
- If cancer cells are found, more lymph nodes will be removed and tissue samples will be checked for signs of cancer. This is called a lymphadenectomy.
Radiation therapy
Targeted therapy
Chemotherapy
Immunotherapy
Posssible Side Effects & Risk Factors
Possible Side Effects
- Vitiligo (loss of pigment)
- Skin rash
- Lymphedema
- Thyroid issues
- Colitis
- Itching
- Joint pain
Risk Factors
- Ultraviolet (UV) light exposure
- Fair / Light Skin
- Moles
- Family history of melanoma
- Personal history of melanoma or other skin cancers
- Weakened Immune system
- Older
- Males
Disclaimer: The information in this book/website is for educational purposes only and has been obtained through research, publications and personal experience, and shall not be liable for incorrect information. Any mentioned publications or websites does not imply endorsement. As this industry is ever changing, I urge readers to confirm the information contained in this book/website. The author will not be liable for any injuries sustained from practicing techniques taught or for any typographical errors or omissions.
It is advised that you always check with your medical doctor or physical therapist before starting an exercise program or change in diet.
|
Information and pictures from National Cancer Institute unless otherwise specified |