What are some
Other Cancer Treatments
Your Body is Your Temple
Research, Resources & Education
Table of Contents
Other treatments for cancer can include ablation, watchful waiting, steroids, radioactive iodine, ultrasound therapy and vaccine therapy.
Information from the National Cancer Institute unless otherwise specified
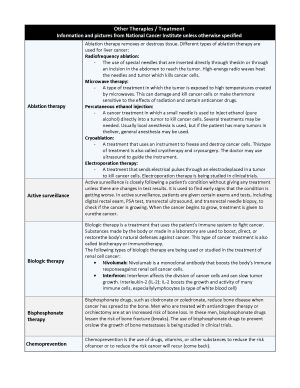
Other Cancer Therapies / Treatments
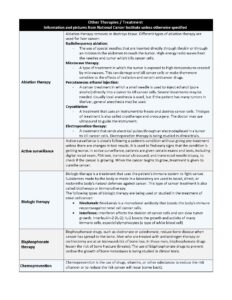
Ablation Therapy
Ablation therapy removes or destroys tissue. Different types of ablation therapy are used for liver cancer:
- Radiofrequency ablation: The use of special needles that are inserted directly through the skin or through an incision in the abdomen to reach the tumor. High-energy radio waves heat the needles and tumor which kills cancer cells.
- Microwave therapy: A type of treatment in which the tumor is exposed to high temperatures created by microwaves. This can damage and kill cancer cells or make them more sensitive to the effects of radiation and certain anticancer drugs.
- Percutaneous ethanol injection: A cancer treatment in which a small needle is used to inject ethanol (pure alcohol) directly into a tumor to kill cancer cells. Several treatments may be needed. Usually local anesthesia is used, but if the patient has many tumors in the liver, general anesthesia may be used.
- Cryoablation: A treatment that uses an instrument to freeze and destroy cancer cells. This type of treatment is also called cryotherapy and cryosurgery. The doctor may use ultrasound to guide the instrument.
- Electroporation therapy: A treatment that sends electrical pulses through an electrode placed in a tumor to kill cancer cells. Electroporation therapy is being studied in clinical trials.
Active Surveillance
Active surveillance is closely following a patient’s condition without giving any treatment unless there are changes in test results.
- It is used to find early signs that the condition is getting worse.
- In active surveillance, patients are given certain exams and tests, including digital rectal exam, PSA test, transrectal ultrasound, and transrectal needle biopsy, to check if the cancer is growing.
- When the cancer begins to grow, treatment is given to cure the cancer.
Biologic Therapy
Biologic therapy is a treatment that uses the patient’s immune system to fight cancer. Substances made by the body or made in a laboratory are used to boost, direct, or restore the body’s natural defenses against cancer. This type of cancer treatment is also called biotherapy or immunotherapy.
The following types of biologic therapy are being used or studied in the treatment of renal cell cancer:
- Nivolumab: Nivolumab is a monoclonal antibody that boosts the body’s immune response against renal cell cancer cells.
- Interferon: Interferon affects the division of cancer cells and can slow tumor growth.
- Interleukin-2 (IL-2): IL-2 boosts the growth and activity of many immune cells, especially lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell)
Bisphosphonate Therapy
Bisphosphonate drugs, such as clodronate or zoledronate, reduce bone disease when cancer has spread to the bone.
- Men who are treated with antiandrogen therapy or orchiectomy are at an increased risk of bone loss. In these men, bisphosphonate drugs lessen the risk of bone fracture (breaks).
The use of bisphosphonate drugs to prevent or slow the growth of bone metastases is being studied in clinical trials.
Chemoprevention
Chemoprevention is the use of drugs, vitamins, or other substances to reduce the risk of cancer or to reduce the risk cancer will recur (come back).
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell Therapy
CAR T-cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy that changes the patient’s T cells (a type of immune system cell) so they will attack certain proteins on the surface of cancer cells.
- T cells are taken from the patient and special receptors are added to their surface in the laboratory. The changed cells are called chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells.
- The CAR T cells are grown in the laboratory and given to the patient by infusion.
- The CAR T cells multiply in the patient’s blood and attack cancer cells.
CAR T-cell therapy is being studied in the treatment of adult ALL that has recurred (come back).
Electrocautery
Electrocautery is a treatment that uses a probe or needle heated by an electric current to destroy abnormal tissue.
For tumors in the airways, electrocautery is done through an endoscope.
Embolization Therapy (Liver). Aka Chemoembolization
Embolization therapy is the use of substances to block or decrease the flow of blood through the hepatic artery to the tumor. When the tumor does not get the oxygen and nutrients it needs, it will not continue to grow.
- Embolization therapy is used for patients who cannot have surgery to remove the tumor or ablation therapy and whose tumor has not spread outside the liver.
The liver receives blood from the hepatic portal vein and the hepatic artery. Blood that comes into the liver from the hepatic portal vein usually goes to the healthy liver tissue. Blood that comes from the hepatic artery usually goes to the tumor. When the hepatic artery is blocked during embolization therapy, the healthy liver tissue continues to receive blood from the hepatic portal vein. ”
There are two main types of embolization therapy:
- Transarterial embolization (TAE): A small incision (cut) is made in the inner thigh and a catheter (thin, flexible tube) is inserted and threaded up into the hepatic artery. Once the catheter is in place, a substance that blocks the hepatic artery and stops blood flow to the tumor is injected.
- Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE): This procedure is like TAE except an anticancer drug is also given.
- The procedure can be done by attaching the anticancer drug to small beads that are injected into the hepatic artery or by injecting the anticancer drug through the catheter into the hepatic artery and then injecting the substance to block the hepatic artery.
- Most of the anticancer drug is trapped near the tumor and only a small amount of the drug reaches other parts of the body.
- This type of treatment is also called chemoembolization.
Endoscopic Stent Placement
An endoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument used to look at tissues inside the body. An endoscope has a light and a lens for viewing and may be used to place a stent in a body structure to keep the structure open.
- An endoscopic stent can be used to open an airway blocked by abnormal tissue.
High-Intensity–Focused Ultrasound Therapy
High-intensity–focused ultrasound therapy is a treatment that uses ultrasound (high- energy sound waves) to destroy cancer cells.
- To treat prostate cancer, an endorectal probe is used to make the sound waves.
Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
Monoclonal antibody therapy is a cancer treatment that uses antibodies made in the laboratory, from a single type of immune system cell.
- These antibodies can identify substances on cancer cells or normal substances that may help cancer cells grow.
- The antibodies attach to the substances and kill the cancer cells, block their growth, or keep them from spreading.
- Monoclonal antibodies are given by infusion.
- They may be used alone or to carry drugs, toxins, or radioactive material directly to cancer cells.
Proton Beam Radiation Therapy
Proton beam radiation therapy is a type of high-energy, external radiation therapy that targets tumors with streams of protons (small, positively charged particles).
This type of radiation therapy is being studied in the treatment of prostate cancer.
Radioactive Iodine
A radioactive form of iodine, often used for imaging tests or to treat an overactive thyroid, thyroid cancer, and certain other cancers.
- For imaging tests, the patient takes a small dose of radioactive iodine that collects in thyroid cells and certain kinds of tumors and can be detected by a scanner.
- To treat thyroid cancer, the patient takes a large dose of radioactive iodine, which kills thyroid cells.
- Radioactive iodine is also used in internal radiation therapy for prostate cancer, intraocular (eye) melanoma, and carcinoid tumors.
- Radioactive iodine is given by mouth as a liquid or in capsules, by infusion, or sealed in seeds, which are placed in or near the tumor to kill cancer cells.
Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation is the use of a special probe with tiny electrodes that kill cancer cells.
- Sometimes the probe is inserted directly through the skin and only local anesthesia is needed.
- In other cases, the probe is inserted through an incision in the abdomen. This is done in the hospital with general anesthesia.
Radiopharmaceutical Therapy
Radiopharmaceutical therapy uses a radioactive substance to treat cancer. Radiopharmaceutical therapy includes the following:
- Alpha emitter radiation therapy uses a radioactive substance to treat prostate cancer that has spread to the bone.
- A radioactive substance called radium-223 is injected into a vein and travels through the bloodstream. The radium-223 collects in areas of bone with cancer and kills the cancer cells.
Radiosensitizers
Radiosensitizers are substances that make tumor cells easier to kill with radiation therapy.
The combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy given with a radiosensitizer is being studied in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.
Steroid Therapy
Steroids are hormones made naturally in the body by the adrenal glands and by reproductive organs. Some types of steroids are made in a laboratory.
- Certain steroid drugs have been found to help chemotherapy work better and help stop the growth of cancer cells.
- Steroids can also help the lungs of the fetus develop faster than normal. This is important when delivery is induced early.
Vaccine Therapy
Vaccine therapy uses a substance or group of substances meant to cause the immune system to respond to a tumor and kill it.
Vaccine therapy is being studied in the treatment of stage III melanoma that can be removed by surgery.
Watchful Waiting
Watchful waiting is closely monitoring a patient’s condition without giving any treatment until signs or symptoms appear or change. This is also called observation. During this time, problems caused by the disease, such as infection, are treated.
Disclaimer: The information in this book/website is for educational purposes only and has been obtained through research, publications and personal experience, and shall not be liable for incorrect information. Any mentioned publications or websites does not imply endorsement. As this industry is ever changing, I urge readers to confirm the information contained in this book/website. The author will not be liable for any injuries sustained from practicing techniques taught or for any typographical errors or omissions.
It is advised that you always check with your medical doctor or physical therapist before starting an exercise program or change in diet.
Information and pictures from National Cancer Institute unless otherwise specified
|