What is Cancer?
Your Body is Your Temple
Research, Resources & Education
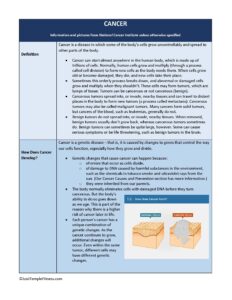
Cancer is a disease in which some of the body’s cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body.
Information and pictures from National Cancer Institute |
Cancer Videos
YouTube Videos that help explain What Cancer Is.
Disclaimer:
This is for research only and Lost Temple Fitness & Cancer does not endorse any video presented on this website.
It is advised that you ALWAYS CHECK WITH YOUR PHYSICIAN for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
What is Cancer?
Description, Development and How & When is Spreads
Cancer is a disease in which some of the body’s cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body.
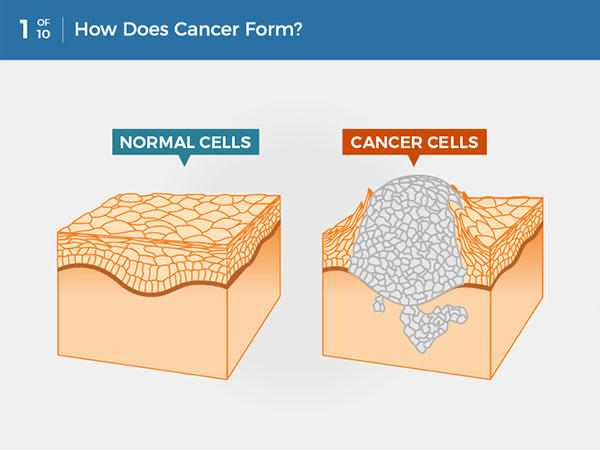
- Cancer can start almost anywhere in the human body, which is made up of trillions of cells.
- Normally, human cells grow and multiply (through a process called cell division) to form new cells as the body needs them.
- When cells grow old or become damaged, they die, and new cells take their place.
- Sometimes this orderly process breaks down, and abnormal or damaged cells grow and multiply when they shouldn’t.
- These cells may form tumors, which are lumps of tissue.
- Tumors can be cancerous or not cancerous (benign).
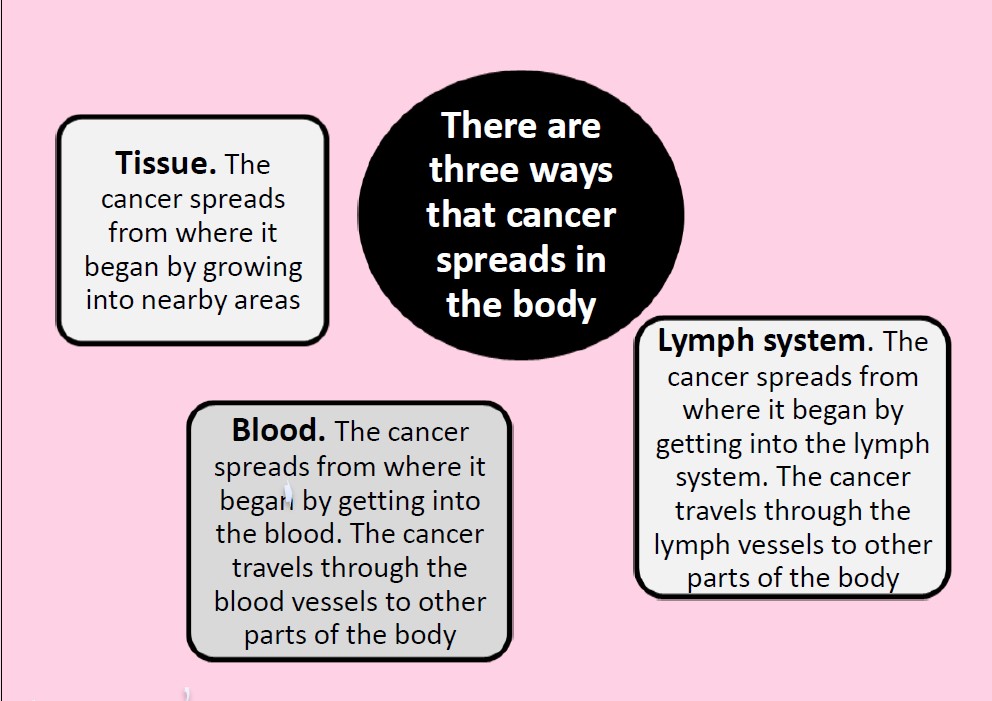
- Cancerous tumors spread into, or invade, nearby tissues and can travel to distant places in the body to form new tumors (a process called metastasis).
- Cancerous tumors may also be called malignant tumors.
- Many cancers form solid tumors, but cancers of the blood, such as leukemias, generally do not.
- Benign tumors do not spread into, or invade, nearby tissues.
- When removed, benign tumors usually don’t grow back, whereas cancerous tumors sometimes do.
- Benign tumors can sometimes be quite large, however.
- Some can cause serious symptoms or be life threatening, such as benign tumors in the brain.
Cancer is a genetic disease—that is, it is caused by changes to genes that control the way our cells function, especially how they grow and divide.
- Genetic changes that cause cancer can happen because:
- of errors that occur as cells divide.
- of damage to DNA caused by harmful substances in the environment, such as the chemicals in tobacco smoke and ultraviolet rays from the sun.
- they were inherited from our parents.
- The body normally eliminates cells with damaged DNA before they turn cancerous.
- But the body’s ability to do so goes down as we age.
- This is part of the reason why there is a higher risk of cancer later in life.
- Each person’s cancer has a unique combination of genetic changes.
- As the cancer continues to grow, additional changes will occur.
- Even within the same tumor, different cells may have different genetic changes.
- A cancer that has spread from the place where it first formed to another place in the body is called metastatic cancer.
- The process by which cancer cells spread to other parts of the body is called metastasis.
- Metastatic cancer has the same name and the same type of cancer cells as the original, or primary, cancer.
- For example, breast cancer that forms a metastatic tumor in the lung is metastatic breast cancer, not lung cancer.
- Under a microscope, metastatic cancer cells generally look the same as cells of the original cancer.
- Moreover, metastatic cancer cells and cells of the original cancer usually have some molecular features in common, such as the presence of specific chromosome changes.
- In some cases, treatment may help prolong the lives of people with metastatic cancer.
- In other cases, the primary goal of treatment for metastatic cancer is to control the growth of the cancer or to relieve symptoms it is causing.
- Metastatic tumors can cause severe damage to how the body functions, and most people who die of cancer die of metastatic disease.
Disclaimer: The information in this book/website is for educational purposes only and has been obtained through research, publications and personal experience, and shall not be liable for incorrect information. Any mentioned publications or websites does not imply endorsement. As this industry is ever changing, I urge readers to confirm the information contained in this book/website. The author will not be liable for any injuries sustained from practicing techniques taught or for any typographical errors or omissions.
It is advised that you always check with your medical doctor or physical therapist before starting an exercise program or change in diet.